Knee pain
Knee pain is, along with back and neck pain, the most common physical complaints we see in practice. Pain in the knee often occurs in older people in relation to wear and tear of the joint. In younger people, we often see knee pain occurring during sports.
Scientific research has shown that physical therapy is effective for many knee problems. On the one hand, pain can be reduced, but with proper treatment and guidance, limitations in sports or work, for example, are often well resolved.
Knee osteoarthritis
Features
Knee problems as one ages are often related to wear and tear on the joint. The layer of cartilage in the joint becomes thinner. This can be accompanied by pain, stiffness and swelling of the joint, as well as certainly limitations in daily activities.
Causes
As we age, we all get osteoarthritis. So this is not an abnormality or disease. Only when the degree of wear and tear does not match the age can you say it is abnormal.
Treatment
At Fysiotherapie de Jong , we work according to the GLA:D program when treating hip and knee osteoarthritis. The treatment program consists of exercise therapy, explanation of the expected recovery, possible treatment to keep the joint moving properly and guidance on work or sports resumption.
Cruciate ligament injury
Features
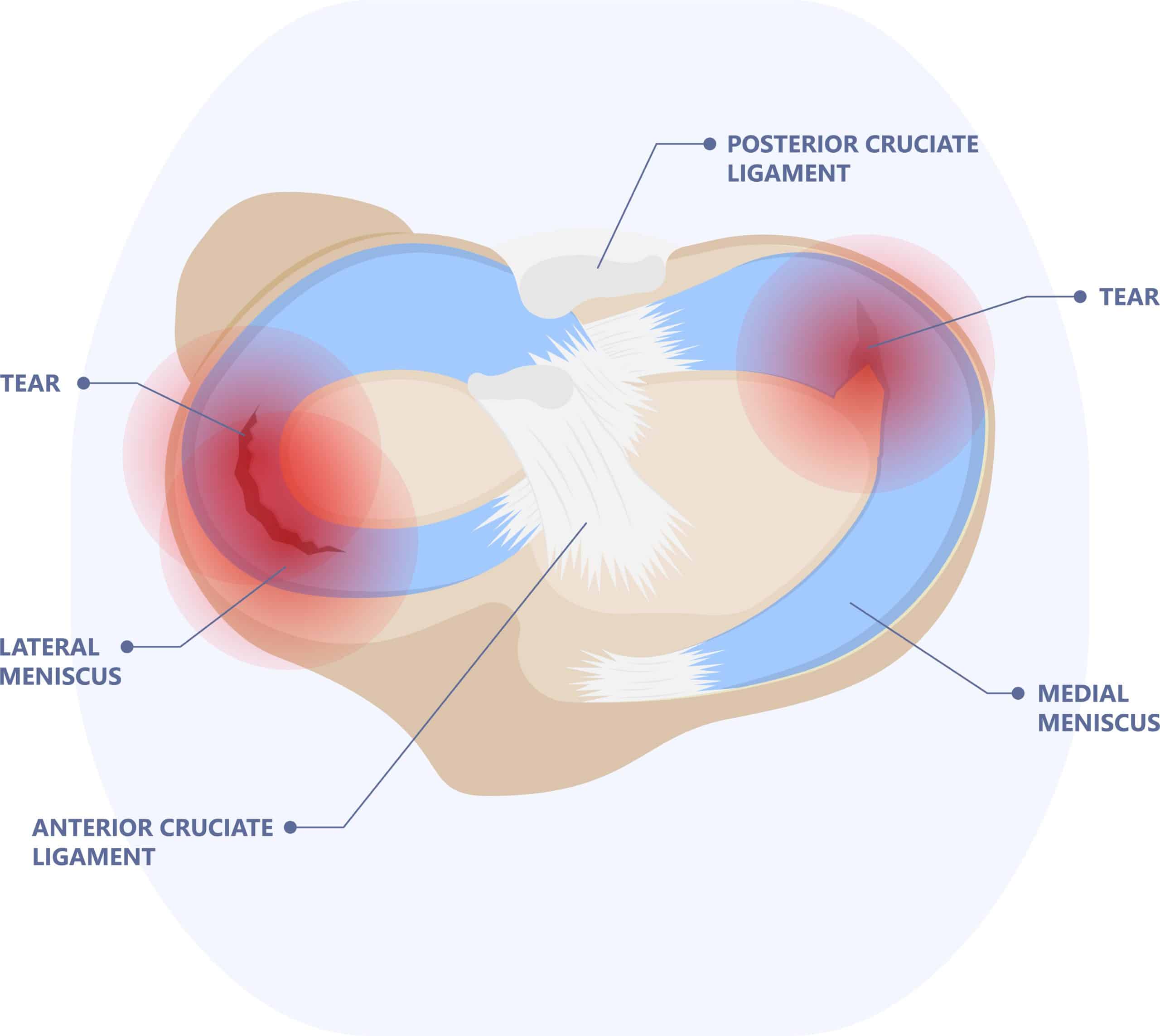
A knee has two cruciate ligaments, an anterior and posterior cruciate ligament. The anterior is much more often involved in injury. The ligament can (tear) during twisting or overstretching of the knee. Tearing the cruciate ligament can make the knee feel unstable. You feel as if you are sinking through the knee.
Diagnosis
You are often referred to the sports doctor or orthopedist after the trauma, who will order an MRI to determine what the damage is in the joint. Whether a torn cruciate ligament requires surgery depends on the perceived instability of the knee and the sports you still want to play. Physical therapy, strength exercises and a brace, for example, may be sufficient to stabilize the joint.
Treatment
If surgery is necessary, physical therapy will play a major role in recovery. The physical therapist will give you guidance in improving the mobility of the joint and in training strength and stability. You will be supervised until you can return to full sports.
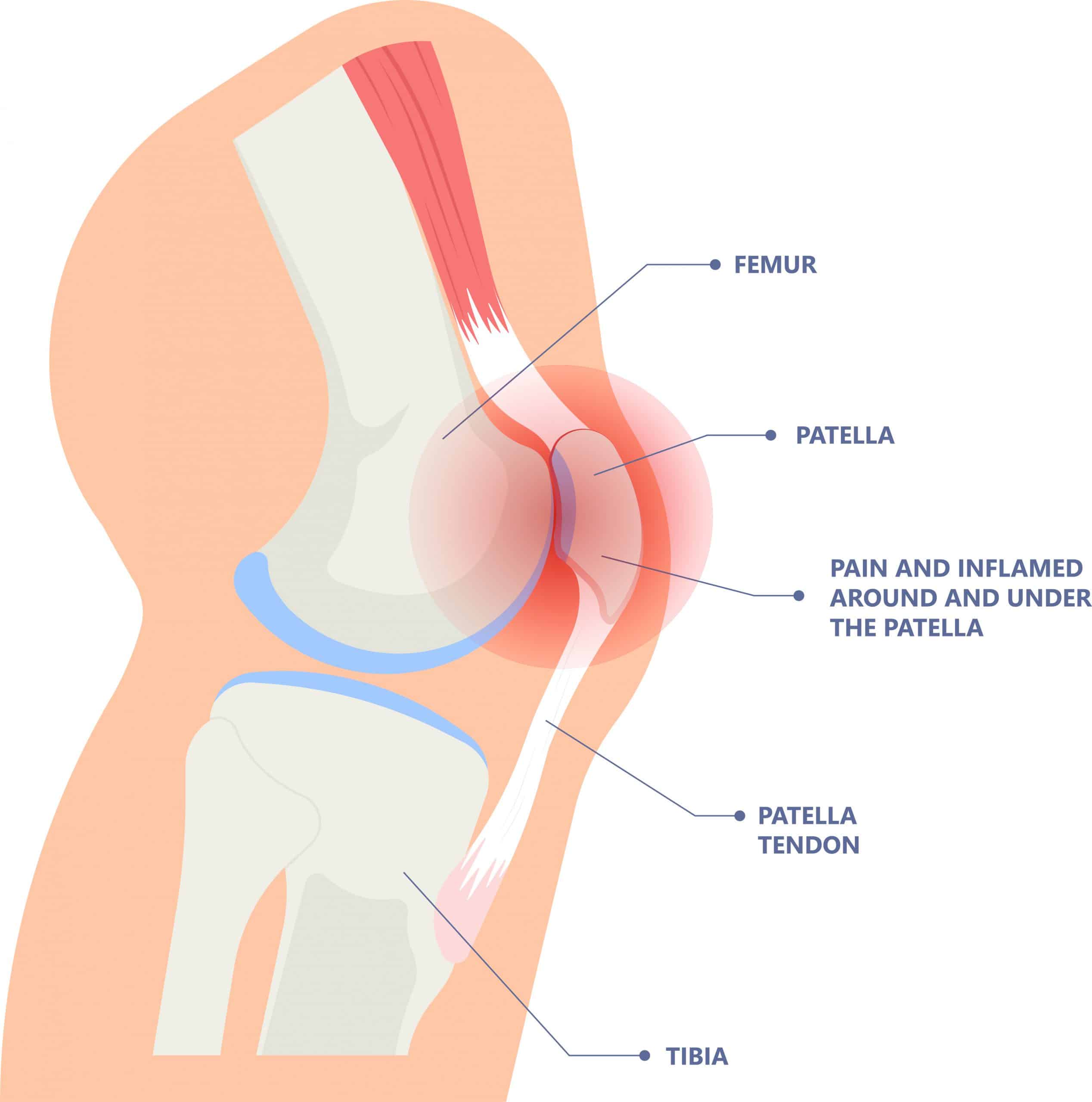
Kneecap pain
Features
These knee problems are common in young people and can have multiple causes. Pain is often present during somewhat heavier loads on the knee, such as sports. Although these complaints do not cause direct damage to the knee joint, the pain can be very annoying.
Causes
Factors that increase the likelihood of these complaints include being overweight, excessive sagging in foot/ankle and heavy loads such as running and lots of jumping. In addition, people with hypermobility are more likely to have complaints around the kneecap.
Treatment
The treatment process often consists of exercise therapy. In addition, we regularly work with a podiatrist to assess whether insoles can support recovery.
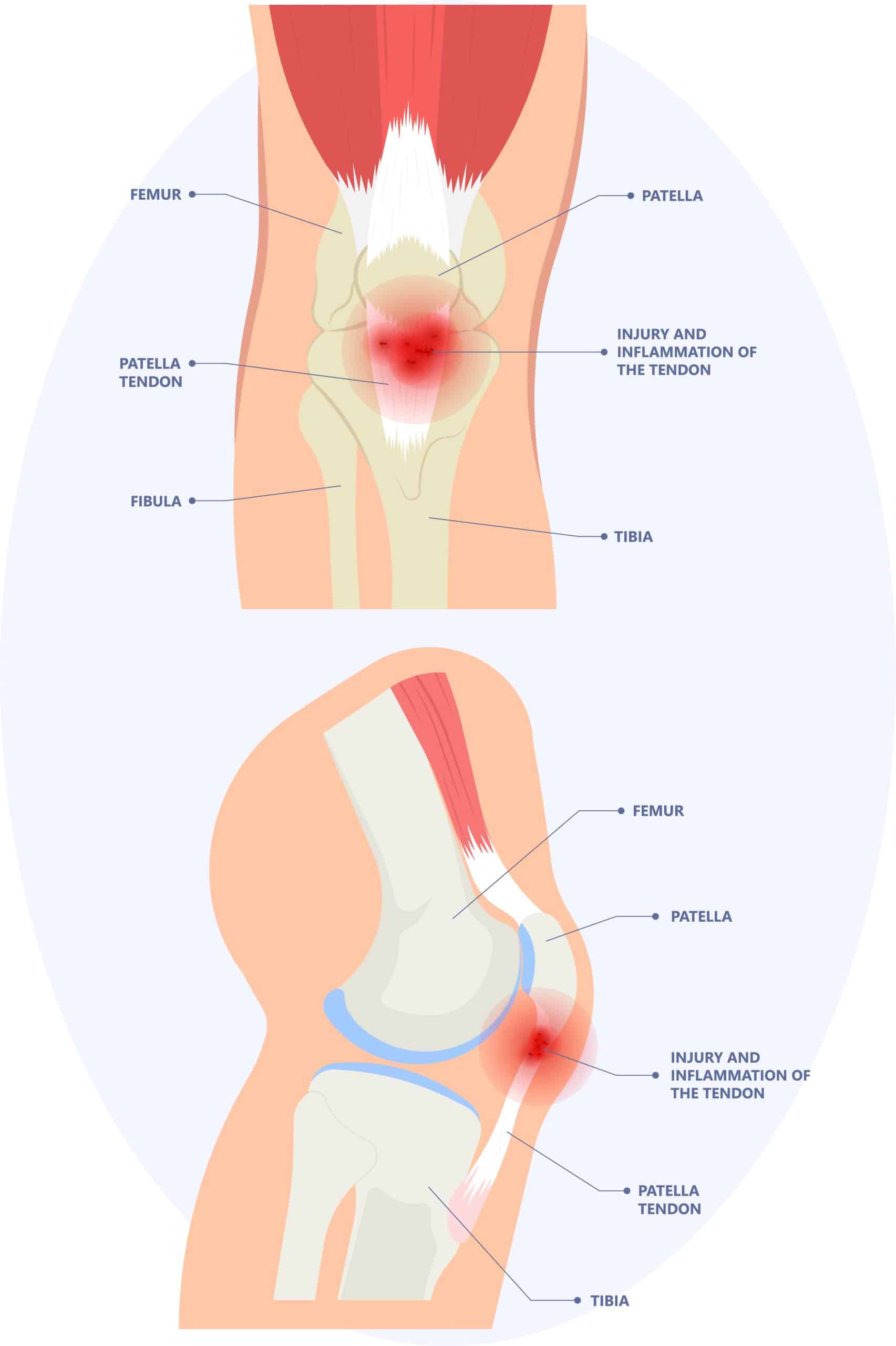
Sweaters Knee
A sweaters knee is most common in sports that involve frequent jumping or a higher peak load on the knee from a lot of turning and turning.
Features
The location of the pain is on the underside of the kneecap at the transition of the patellar tendon into the bone. The pain is often easy to pinpoint in this area. The complaint has several stages. Initially, you can still walk out the pain; once the knee warms up, the pain is no longer really bothersome. Later, however, the pain becomes worse with strain and even requires cessation of activity. The pain can now be present even at rest, while sitting with bent legs. This is why it is sometimes called a "theater knee.
Cause
The complaint is not caused by inflammation, which is often thought, but by a kind of wear and tear process of the tendon. Through prolonged overuse, something goes wrong in the repair process of the patellar tendon. As a result, the quality of the tendon gradually decreases, eventually causing symptoms.
Treatment
Treatment consists of identifying movement limitations in the knee's chain of motion. That is, the foot, hip, pelvis and low back are also looked at. This is combined with strength training to increase the load capacity of the tendon. If necessary, this process can be supported with EPTE to boost tendon quality recovery. The total recovery from such a tendon injury takes about 3 months.
Meniscus injury
The meniscus is an 8-shaped piece of cartilage located in the knee. The function of this cartilage is to enlarge the joint surface so that forces are better distributed, and it allows for better lubrication of the joint.
Characteristics and cause
We distinguish in meniscus injuries between acute injuries and so-called degenerative injuries. Acute injury occurs as a result of knee trauma where large forces are applied to the knee. The knee then often becomes thick within the first 24 hours after the injury occurs. Locking symptoms may then develop, that is, the knee no longer moves properly because something seems to be stuck in the joint.
In degenerative injuries, the meniscus slowly deteriorates in quality, as does the rest of the knee. This often causes pain with loading, twisting or squatting and can also cause swelling of the knee. Sometimes it also becomes more difficult to bend or extend the knee.
Treatment
When lock symptoms become bothersome, a referral to an orthopedist is recommended to assess your eligibility for surgery. Meniscus surgery is performed with keyhole surgery and recovery takes approximately 3-6 months. To return to your sports level, postoperative rehabilitation with a (sports) physical therapist is recommended.
Surgery for a degenerative meniscus has been shown to be less effective than treatment with muscle-strengthening exercises under the guidance of a physical therapist. This may possibly be supported with anti-inflammatories.
Research and treatment
The physical therapist will assess your symptoms through an interview and focused examination. Then the diagnosis will be discussed with you and a personalized treatment plan will be drawn up.
Cost
Physical therapy is covered by your supplementary insurance. Don't have supplementary insurance? Then we apply the following rates.
After surgery, from the 21st time, treatment is reimbursed from basic insurance (as long as medically necessary up to one year after surgery date).
For Coverage osteoarthritis knee click here.
GP/specialist referral
Would you like to make an appointment regarding any of the above complaints? You can contact us directly.