Dizziness
Dizziness symptoms can have a considerable impact on a person's daily life. Work, sports but also just everyday activities can be significantly limited, forcing people to be less and less active.
Dizziness is the feeling experienced when the relationship to the space around you is disturbed. This can include vertigo, faintness, a balance disorder and, for example, the feeling of a light head. Normally, every person receives constant information about the space around him or her and the body's position in it. In dizziness, this information processing is disturbed.
Dizziness symptoms can have a significant impact on your daily life. Work, sports but also just everyday activities can suffer greatly. This may force you to become less active. There are different types of dizziness. For some, physical therapy can help with the cause of the dizziness and for some, physical therapy can help reduce the effects of the dizziness.
Cervicogenic dizziness
Features
Cervicogenic dizziness can last from minutes to hours and is usually accompanied by neck pain, such as pain or stiffness but can also produce nausea or blurred vision. Symptoms increase with movements of the head and after holding the same head position for a long time. In some cases, there is also ear pain or balance problems.
Cause
Cervicogenic vertigo occurs as a result of a movement problem in the neck and head. This may involve decreased mobility of the neck, increased muscle tension in the neck or arthrosis (wear and tear) of cervical vertebrae.
Treatment
If you suffer from cervicogenic vertigo, your physical therapist can help by improving the mobility of the cervical vertebrae, providing relaxation in the neck muscles and giving advice on (work) posture and movement.
Benign Paroxysmal Position Dizziness (BPPD)
Features
BPPD stands for Benign Paraparoxymal Positional Dizziness and is a vertigo caused by movements of the head. Examples include turning the head or sitting up from lying down. The dizziness is severe and usually subsides within a minute.
Cause
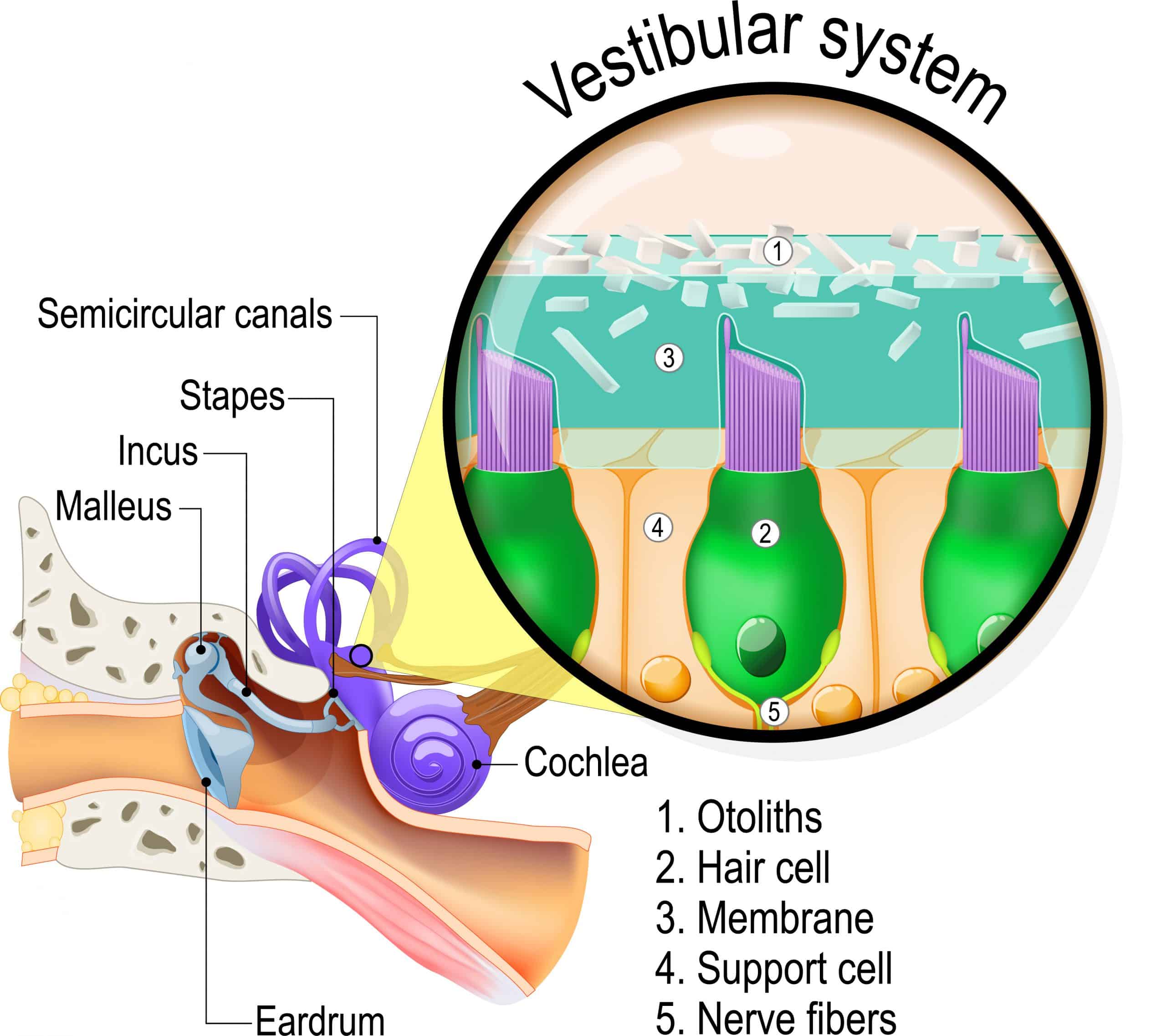
The cause of BPPD is not yet completely clear. Presumably, grit develops in the tubes of our balance organ. This organ is located in our inner ear and contains fluid. The grit prevents fluid in the organ from moving properly during movements of the head, resulting in dizziness.
Treatment
Although BPPD is a harmless condition, it can be very annoying. Fortunately, there is an effective treatment. This involves the use of exercises (Epley maneuver), which cause the grit to move to a place where it can no longer cause discomfort. Your physical therapist will do these exercises with you and also give advice, which you can work with at home.
Ménière's disease
Features
This form of vertigo occurs suddenly and is accompanied by tinnitus and (temporarily) impaired hearing. The duration of the symptoms varies considerably: between 20 minutes to a maximum of 12 hours and can occur sporadically, but also weekly. After an attack, you may be slightly dizzy for several days.
Cause
As with BPPD, the cause of Ménière's disease has not yet been determined. Interestingly, the vast majority of people who experience Ménière's also have hearing loss, with low tones usually the first to drop out. Usually, the number of Ménière's attacks decreases with time.
Treatment
If balance problems persist after a vertigo attack, physical therapy can help you regain your balance through exercises and advice on posture and movement, after which both daily and sports activities can be resumed.
Neuritis vestibularis
Features
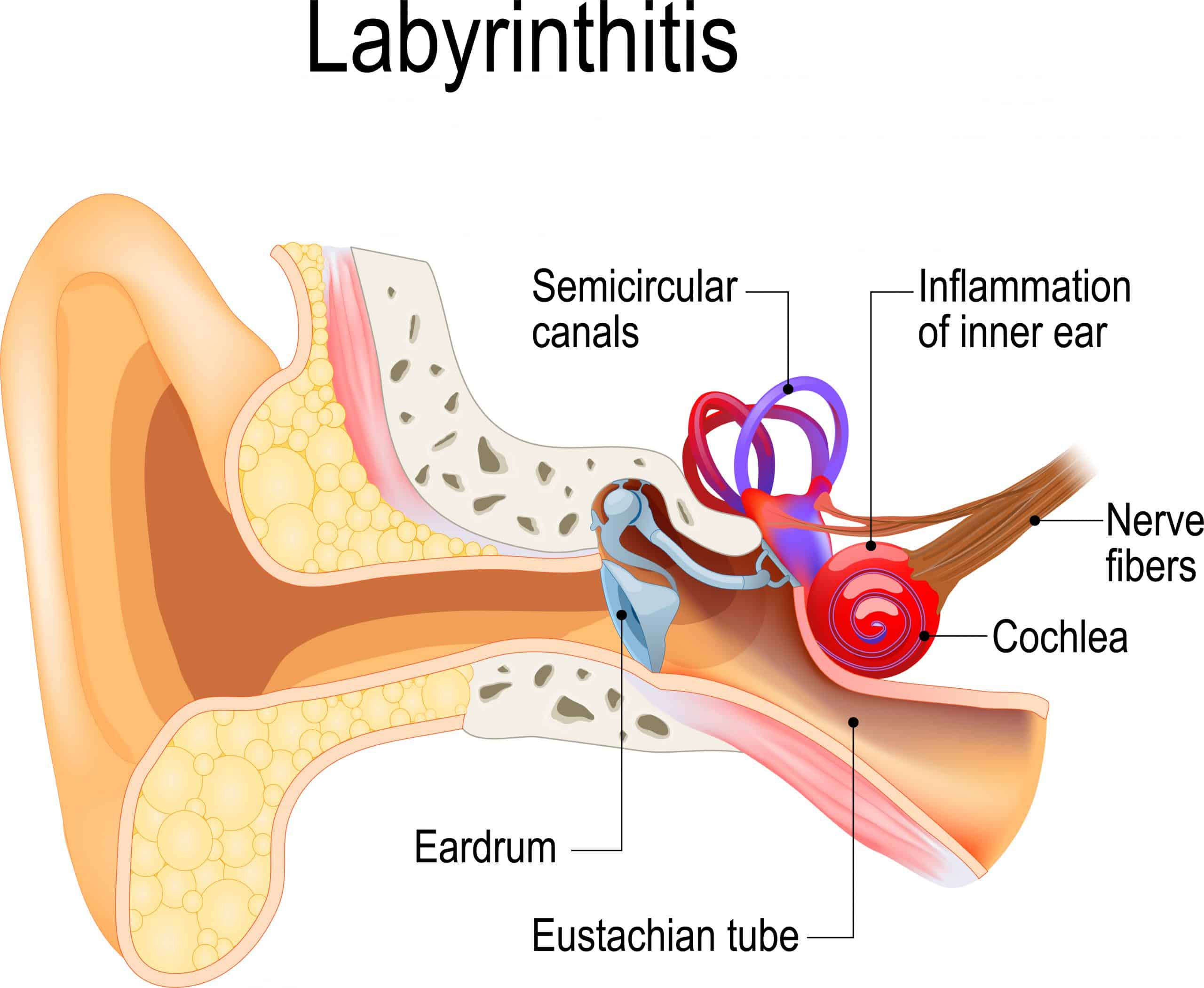
This form of dizziness can last from days to weeks and is often experienced as very intense. In addition to spinning dizziness (feeling like you are spinning around while standing still), it can make you nauseous or even make you vomit. Moving makes the dizziness worse. The symptoms eventually subside slowly, but the dizziness persists for months in some people.
Cause
The dizziness in the case of neuritis vestibularis is caused by the malfunctioning of the balance organ. Sometimes people first have a cold or respiratory infection before the dizziness symptoms appear.
Treatment
As with Ménière's disease, physical therapy can play a role in regaining balance when it has been disrupted after the attack.
Research and treatment
The physical therapist will assess your symptoms through an interview and focused examination. Then the diagnosis will be discussed with you and a personalized treatment plan will be drawn up.
Cost
Physical therapy is covered by your supplementary insurance. Don't have supplementary insurance? Then we apply the following rates.
GP/specialist referral
Would you like to make an appointment regarding one of the above complaints? For this you do not need a referral from your GP or specialist. You can contact us directly.
Within our practice, Evelien Renders, Lotte van Montfort, Natascha Huls and Susanne Rikken specialize in dizziness complaints.