Back Pain
Back pain is a common problem. Often the symptoms are short-lived. But sometimes the symptoms last longer or are chronic. In many cases, the physical therapist can help reduce or even completely resolve back pain.
Back pain comes in different forms. You could speak of specific and nonspecific back pain. With specific back pain, there is an abnormality in the low back that can explain the symptoms. Like a herniated disc. With non-specific back pain no clear abnormality is found on an MRI, for example. This usually mainly involves weakening of the muscles around the low back.
Acute back pain
Features
Many people experience acute back pain sometime in their lives. Often this happens during everyday movements that are not at all strenuous, such as putting on pants. Suddenly you feel a stabbing pain in the back, after which you can hardly move your back.
Causes
Often a heavy workload has preceded it. People have worked hard the day before, or dug up the garden. The back muscles are fatigued, so it can suddenly shoot into the back just like that. This shooting pain is mainly caused by massive cramping of muscles in the lower back.
Diagnosis
The physical therapist will primarily investigate whether it is a cramping of the muscles and possible joint restriction in the low back. Should there be more to it, it can always be discussed with the family doctor.
Treatment
Acute back pain often recovers on its own within 1-2 weeks. We will offer advice on what you can do yourself to stimulate recovery. If recovery is not as expected, we can support it. For example, with manual therapy and exercises. If the back muscles appear to be too weak we will start an exercise program.
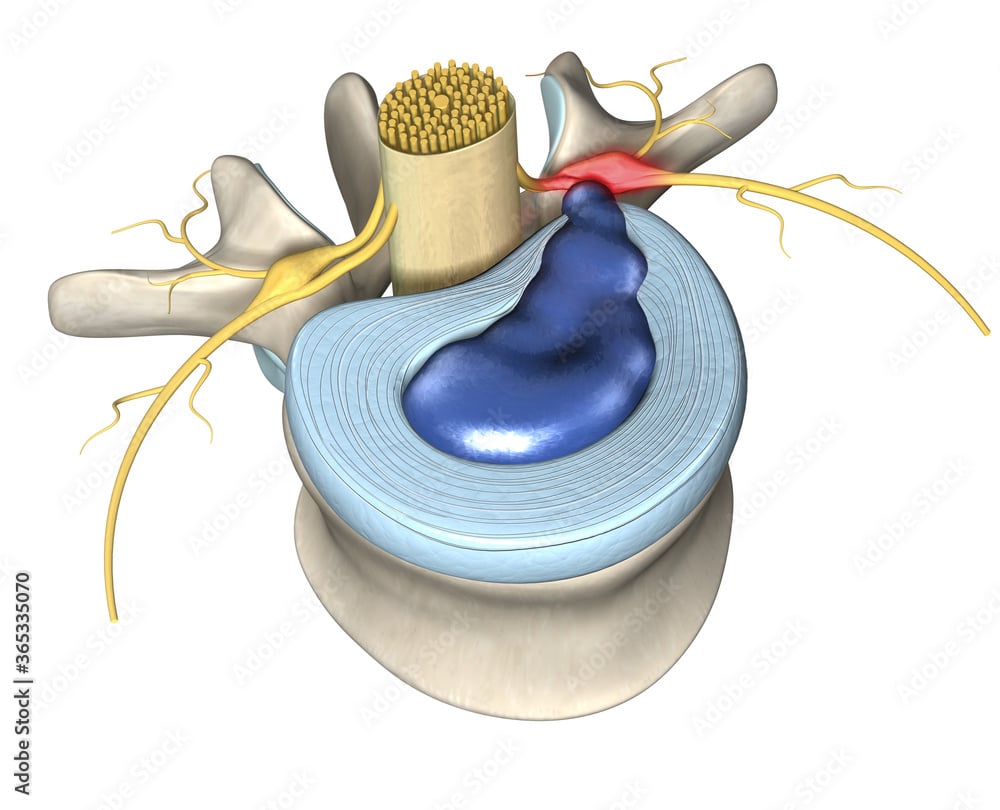
Hernia
Features
A herniated disc is a bulge of an intervertebral disc. These intervertebral discs are located in the back between the vertebrae. When an intervertebral disc bulges, an inflammatory process often develops first. This can irritate the nerve pathway that runs from the back to the leg. This causes radiating pain in the leg. If the bulge gets bigger then it can itself start to press against the nerve, giving you an increase in symptoms.
Cause
There are several factors that play a role in the development of a herniated disc. Frequent sitting is one of them, but also, for example, poor posture, obesity and genetic predisposition.
Diagnosis
To demonstrate a herniated disc, in addition to pain symptoms, any loss of strength in the leg, loss of sensation in the leg and of reflexes are examined. Based on these, a diagnosis could already be made. An MRI scan can provide absolute certainty, but it is often not necessary.
Treatment
A herniated disc is often very painful, but usually harmless. In most people, pain symptoms recover within 6-12 weeks. The important thing is that you do keep moving. The pain gets less with patience; you do not have to take bed rest for this. Medication (anti-inflammatories) can help and physical therapy can also stimulate recovery.
Our physical therapists with specialization in treating the back can support you. If you have any questions, please let us know!
Research and treatment
The physical therapist will assess your symptoms through an interview and focused examination. Then the diagnosis will be discussed with you and a personalized treatment plan will be drawn up.
Cost
Physical therapy is covered by your supplementary insurance. Don't have supplementary insurance? Then we apply the following rates.
GP/specialist referral
Would you like to make an appointment regarding one of the above complaints? For this you do not need a referral from your GP or specialist. You can contact us directly.