COPD
COPD stands for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, this name includes both pulmonary emphysema and chronic bronchitis. Both are health conditions in which breathing becomes more difficult.
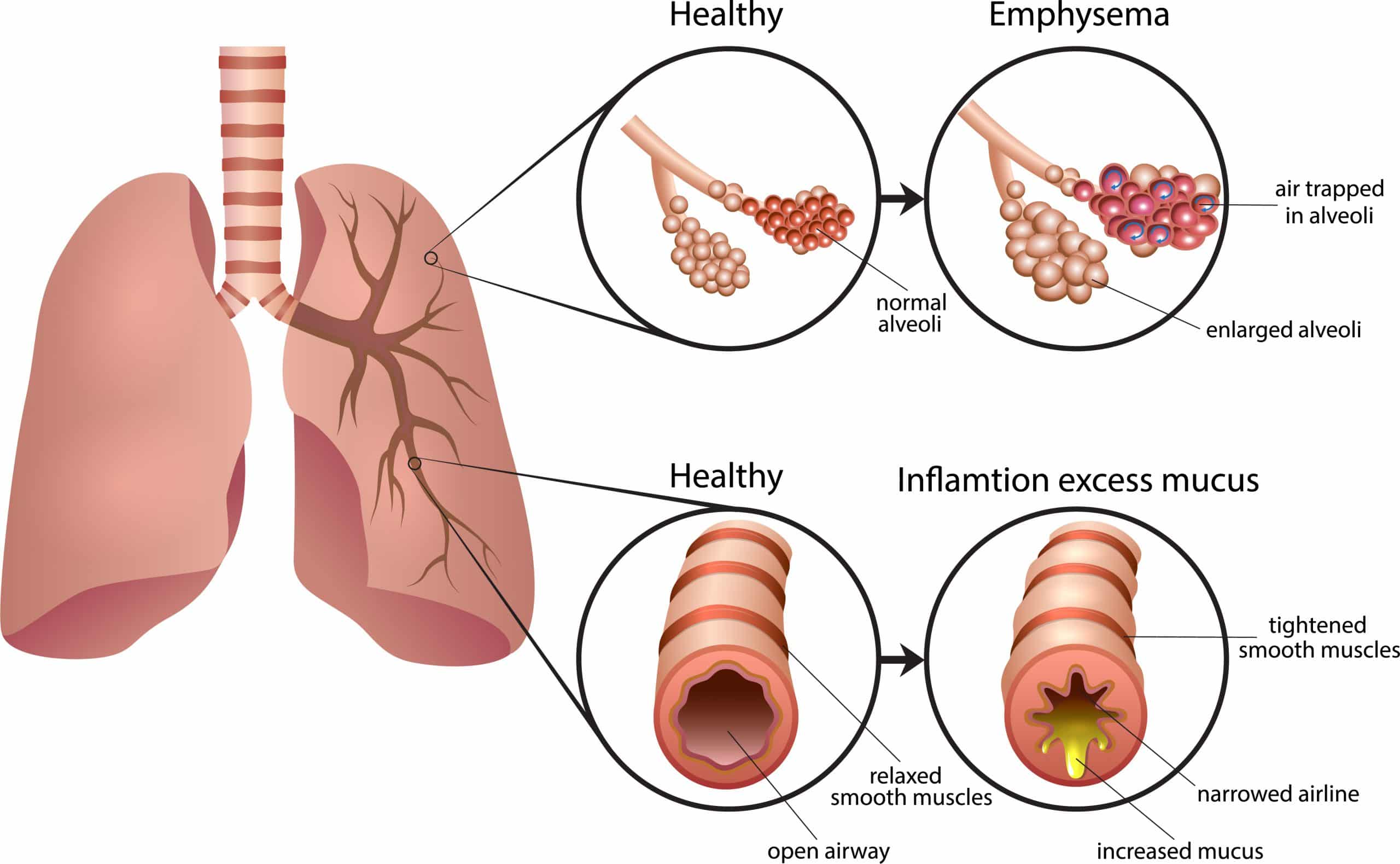
Pulmonary emphysema
Pulmonary emphysema involves the destruction of the alveoli of the lungs. These are the parts of the lungs that provide the actual transfer of oxygen into the bloodstream and waste products out of the bloodstream. You can think of these as a kind of stretchy balloon; they can expand and contract again.
With pulmonary emphysema, there is a loss of elasticity of these alveoli and with it a loss of transfer of oxygen and waste products. An additional disadvantage can also be that the walls of the alveoli collapse so that air can no longer escape, this is called air trapping. As a result, mucus can no longer be removed properly and pneumonia can occur more easily.
Chronic bronchitis
The way to the lungs is through the mouth, to the trachea through the bronchi. In chronic bronchitis, the latter are continuously inflamed. This leads to a thickening of the mucus layer and thus a narrowing of the airways. Consequently, breathing costs more energy. In healthy people, the respiratory muscles' share of total oxygen consumption does not exceed 5%. In severe COPD patients this can increase to 40%.
Causes
The disease is caused by long-term exposure to outside harmful substances. Smoking is the most common cause, working with chemicals or working in an environment with harmful substances can also be a possible cause.
Characteristics COPD
With COPD, you may suffer from:
- Tightness
- Cough
- Coughing up mucus
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Little muscle strength
- Weight change
Treatment
It is possible to inhibit deterioration through proper treatment. In addition to medication, nutrition and healthy lifestyle, physical therapy plays an important role. You start with individual sessions. Depending on the degree of COPD, you then train twice a week in a group.
Cost
Treatment of COPD is reimbursed from basic insurance (info 2023). You may still receive a bill for the (compulsory) deductible.
GP/specialist referral
Treatment of COPD requires a referral. This is obtained through the general practitioner or specialist.
Within our practice, Natascha Huls, Vincent KluitmansandEvelien Renders have specialized in the exercise program for COPD patients. You can make an appointment online using the button below or by phone.